How You Use Steel Wire for Bonsai Shaping
Yes, steel wire can be used for bonsai. It offers remarkable tensile strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion.
Ideal for supporting heavier branches and maintaining intricate shapes, steel wire ensures longevity. However, its limited flexibility and potential to cut into bark require careful monitoring and precise application.
Using the appropriate thickness and regular checks can mitigate potential risks to tree health. While it might be less user-friendly than aluminum or copper wire, steel wire's strength and reusability make it a viable option for bonsai training.
By exploring further, you can discover the best practices for incorporating steel wire into your bonsai care routine.

Key Takeaways
- Steel wire provides exceptional tensile strength and durability for shaping bonsai branches.
- Galvanized or stainless steel wire offers corrosion resistance, ensuring longevity and structural support.
- Regular monitoring is essential to prevent the wire from cutting into the bark and causing damage.
- Steel wire's limited flexibility requires careful handling to avoid injury to the tree.
- Various thicknesses of steel wire allow for precise adjustments while maintaining the desired shape.
What Is Bonsai Wiring?

Bonsai wiring is an important technique used to guide the growth and shape of a bonsai tree by carefully wrapping wire around its branches and trunk. This method allows practitioners to manipulate the tree's orientation, promoting aesthetically pleasing forms and enhancing the tree's overall visual appeal.
Proper application of wiring involves selecting the suitable thickness and type of wire to guarantee that it is strong enough to hold the branch in place but gentle enough to avoid damaging the bark or underlying tissues. The wire must be applied with precision, ensuring that it follows the natural curvature of the branch to avoid stress fractures.
Regular monitoring and timely removal of the wire are crucial to prevent it from cutting into the growing tree.
Types of Bonsai Wire
In the world of bonsai cultivation, choosing the right wire type is essential for effective shaping and growth management. While aluminum and steel wires are frequently used, understanding their unique characteristics, like flexibility and strength, is necessary for the best application.
Moreover, wire thickness choices and precise application methods play important roles in guaranteeing the health and beauty of the bonsai tree.
Aluminum Vs. Steel
When considering the types of wire for bonsai training, understanding the distinct properties and applications of aluminum and steel is essential for ideal tree shaping and health.
Aluminum wire is favored for its flexibility and ease of use, making it suitable for beginners and species with softer bark. It is less likely to damage the tree when applied correctly.
Steel wire, on the other hand, offers superior strength and durability, ideal for larger branches or species with harder, more resilient bark. However, its rigidity can increase the risk of scarring if not meticulously applied.
Each wire type has unique advantages, and the choice between aluminum and steel should be informed by the specific needs of the bonsai and the expertise of the practitioner.
Wire Thickness Options
Selecting the suitable wire thickness is crucial for effective bonsai training, as it directly influences the ability to shape branches without causing undue harm. Different thicknesses serve distinct purposes: thinner wires, typically ranging from 1mm to 2.5mm in diameter, are ideal for delicate and smaller branches, offering sufficient flexibility while minimizing damage.
Thicker wires, from 3mm to 5mm or more, are necessary for larger branches and trunks, providing the strength needed to hold more substantial shapes firmly in place. The choice of wire thickness should align with the branch's size and rigidity, ensuring best control and support during the shaping process.
Understanding these nuances allows bonsai enthusiasts to achieve a harmonious balance between aesthetic form and botanical health.
Application Techniques
Beyond choosing the appropriate wire thickness, understanding the types of bonsai wire available—primarily aluminum and copper—is fundamental for mastering application techniques.
Aluminum wire, known for its pliability and ease of use, is ideal for beginners and species with softer bark. It is also less likely to damage the tree when applied correctly.
Copper wire, on the other hand, offers superior strength and holding power, making it suitable for more experienced practitioners and species with harder bark. When utilized correctly, copper wire can maintain its shape longer, ensuring the desired form is achieved.
Both types of wire have their specific advantages, and selecting the appropriate one depends on the tree species, the practitioner's skill level, and the specific bending requirements.
Properties of Steel Wire

Steel wire is known for its exceptional tensile strength, providing the robust support required for shaping and training bonsai trees. Its corrosion resistance guarantees longevity, even in outdoor environments subject to varying weather conditions.
Additionally, the flexibility and malleability of steel wire allow for precise adjustments, making it an indispensable tool for bonsai enthusiasts.
Tensile Strength Characteristics
Understanding the tensile strength characteristics of steel wire is essential for guaranteeing its effectiveness and reliability in bonsai applications. Tensile strength refers to the maximum amount of tensile stress that a material can withstand before failure.
Steel wire, known for its high tensile strength, provides significant advantages in shaping and supporting bonsai trees. This strength guarantees that the wire can endure the forces exerted by growing branches and trunks without snapping or deforming. Additionally, the robustness of steel wire facilitates more precise and long-lasting training of bonsai structures.
It is imperative to choose the appropriate gauge of steel wire, balancing strength with flexibility, to avoid damaging the delicate vascular system of the bonsai while guiding its growth.
Corrosion Resistance Factors
While the tensile strength of steel wire is paramount for bonsai shaping, its corrosion resistance properties are equally important to guarantee longevity and durability in various environmental conditions. Steel wire used for bonsai must withstand:
- Humidity exposure: Bonsai trees often require frequent watering, creating a consistently moist environment.
- Soil acidity: Some bonsai species thrive in slightly acidic soils, which can accelerate the corrosion process.
- Outdoor elements: Bonsai trees are often displayed outdoors, exposing steel wire to rain, dew, and varying temperatures.
These factors necessitate the use of corrosion-resistant steel types, such as galvanized or stainless steel. Galvanized steel has a protective zinc coating, while stainless steel contains chromium, both of which substantially reduce the risk of rust and prolong the material's usability.
Flexibility and Malleability
The flexibility and malleability of steel wire are crucial attributes that facilitate intricate shaping and positioning of bonsai branches without causing harm to the plant. Steel wire's capacity to bend and twist while preserving its structural integrity makes it a favored choice for bonsai enthusiasts. Its pliability allows for precise adjustments, aiding in the creation of visually pleasing forms.
Additionally, steel wire can withstand the tension needed to direct the growth of branches, guaranteeing they stay in the intended position over time. However, it is essential to choose the suitable gauge of steel wire to strike a balance between strength and flexibility, preventing excessive pressure on the fragile bark and tissues of the bonsai. Proper utilization of these characteristics safeguards the health and attractiveness of the bonsai.
Strength of Steel Wire
Steel wire's unmatched tensile strength makes it a preferred choice for shaping and supporting bonsai trees, guaranteeing both durability and precision in the art of bonsai cultivation. Its strong nature allows it to withstand significant stress without deforming, making it ideal for long-term use.
Unlike softer alternatives, steel wire guarantees that the desired shape of the bonsai remains intact over extended periods.
Key attributes of steel wire include:
- High Tensile Strength: Able to endure substantial force without breaking.
- Durability: Resistant to environmental factors, ensuring longevity.
- Support: Provides strong, reliable support for heavy branches.
These properties make steel wire invaluable for bonsai enthusiasts aiming for meticulous shaping and enduring structural integrity in their miniature trees.
Flexibility of Steel Wire

Flexibility is a critical attribute of steel wire, enabling it to be manipulated with precision to achieve desired plant shapes. The wire's bending capacity allows for meticulous adjustments, ensuring that bonsai branches can be guided into ideal positions without causing damage.
This control over plant shape is fundamental in the art of bonsai, where symmetry and aesthetics are paramount.
Wire Bending Capacity
Evaluating the wire bending capability is vital for bonsai enthusiasts to ensure that the steel wire can be manipulated effectively without compromising the integrity of the plant. Steel wire, recognized for its strength, offers a unique set of characteristics that can be advantageous in bonsai training.
However, understanding its flexibility is essential:
- Gauge Thickness: Thicker steel wire provides superior support but is harder to bend, necessitating more effort and precision.
- Ductility: Highly malleable steel wire can be twisted and turned multiple times without snapping, ensuring longevity in shaping applications.
- Surface Treatment: Galvanized or treated steel wires resist rust, maintain flexibility over time, and prevent damage to the plant's bark.
These factors collectively influence the effectiveness of steel wire in bonsai sculpting.
Plant Shape Control
When utilizing steel wire for bonsai shaping, the ability to precisely control the plant's form hinges on understanding the wire's inherent flexibility and how it interacts with the plant's growth patterns.
Steel wire, known for its strength and rigidity, can exert significant influence on a bonsai's branches. However, its limited flexibility compared to aluminum or copper wire requires careful application. Overly rigid wire may damage delicate branches or restrict natural growth, leading to undesired outcomes.
Selecting the appropriate gauge and applying the wire with precision is essential. Regular monitoring is important to make sure that the wire does not cut into the bark as the plant grows, thereby maintaining the health and aesthetic of the bonsai.
Corrosion Resistance
Steel wire's corrosion resistance is a critical factor in its suitability for use in bonsai cultivation, particularly due to the prolonged exposure to moisture and varying environmental conditions. Corrosion can lead to several issues that affect the integrity and functionality of the wire over time. Properly understanding the types of steel wire available and their respective resistance levels is crucial.
Galvanized steel:
Coated with zinc, offers enhanced protection against rust.
Stainless steel:
Comprises chromium, providing superior corrosion resistance.
Untreated steel:
Prone to rust, especially in humid or rainy climates.
Using steel wire with high corrosion resistance ensures longevity and effectiveness in training bonsai trees, reducing the risk of wire degradation that could compromise structural support.
Effects on Tree Health
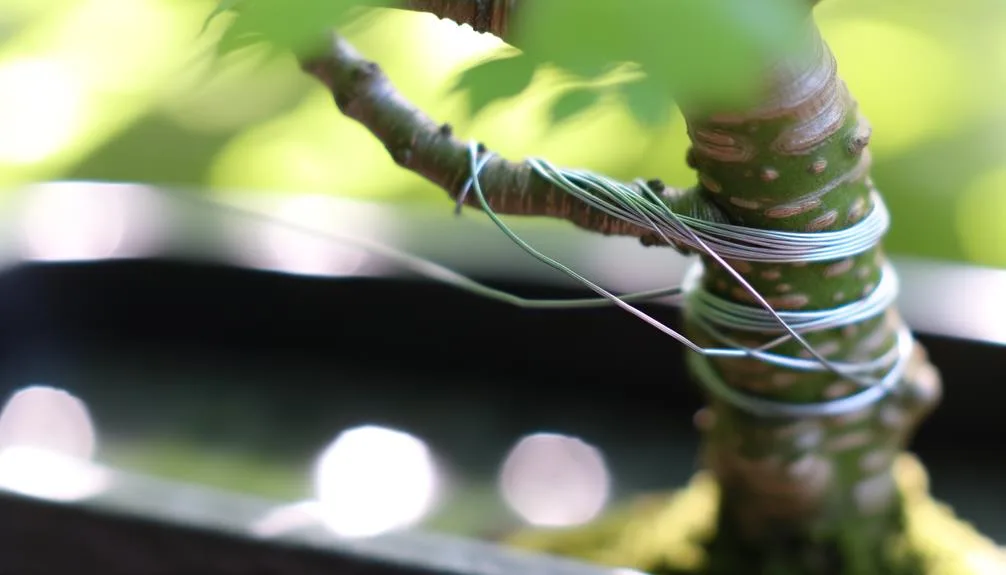

Ensuring that the wire used does not adversely affect the tree's health is essential in bonsai cultivation, as the wire remains in direct contact with the plant for extended periods. Steel wire, while durable, can pose risks to the tree's health if not monitored carefully. Its rigidity can cause injury to the bark and underlying tissues if not adjusted regularly. Additionally, steel wire can rust, leading to potential toxicity and damage to the tree.
Proper application technique is vital; wires should be wrapped loosely to allow for growth, and regular inspections are necessary to prevent constriction. Using a protective layer, such as rubber tubing, can mitigate direct contact, thereby reducing potential harm to the tree's health.
Appearance Considerations
The visual impact of steel wire on bonsai trees must be carefully balanced with the functional requirements of shaping and training the plant. Though steel wire offers strength and durability, its appearance can be intrusive if not applied thoughtfully.
Key considerations include:
- Visibility: Steel wire is more conspicuous than traditional copper or aluminum wiring, potentially detracting from the natural aesthetics.
- Rusting: Over time, steel wire can rust, leading to unsightly discoloration and potential harm to the tree.
- Thickness: Steel wire's rigidity necessitates a larger gauge, which can appear bulky and overpower the delicate structure of the bonsai.
Professionals must weigh these visual aspects against the wire's benefits, ensuring the bonsai's beauty is not compromised.
Cost Comparison
Although steel wire offers certain advantages in strength and durability for bonsai training, it is often more expensive compared to traditional copper or aluminum alternatives. The higher cost of steel wire can be attributed to its manufacturing process and the raw materials involved.
Copper wire, particularly annealed copper, provides excellent flexibility and is widely utilized for its cost-effectiveness. Aluminum wire is another popular choice due to its affordability and ease of use.
For hobbyists and professional bonsai enthusiasts, the increased expense of steel wire may not justify its benefits, especially when considering the frequent need for rewiring as the tree grows. Hence, budget constraints often lead bonsai practitioners to favor copper or aluminum over steel, balancing cost with functionality.
Ease of Use
Steel wire, while robust, presents challenges regarding ease of use due to its rigidity and difficulty to manipulate compared to copper or aluminum alternatives. The inherent stiffness of steel requires greater physical effort, making it less suitable for delicate branches. This rigidity can result in potential damage to the tree if not handled with utmost care.
Increased Physical Effort: The strength of steel demands more force, which can be taxing over prolonged periods.
Limited Flexibility: Unlike softer metals, steel does not easily conform to intricate bends, restricting finer shaping.
Risk of Bark Damage: The hardness of steel can lead to abrasions on the tree bark if not meticulously applied.
These factors highlight why steel wire, despite its durability, may not be the most user-friendly option for bonsai enthusiasts.
Expert Opinions

Recognizing these challenges, many bonsai experts advocate for the use of aluminum or copper wire over steel due to their superior malleability and reduced risk of damaging the tree. The consensus among professionals is grounded in both practical experience and horticultural science. Aluminum wire is praised for its ease of manipulation, making it suitable for beginners and complex designs. Copper wire, while harder to manipulate, offers superior holding power, ideal for more robust shaping. Conversely, steel wire is often considered too rigid and prone to causing bark damage, which can lead to tree stress and potential health issues.
| Wire Type | Malleability | Risk of Damage |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | High | Low |
| Copper | Moderate | Moderate |
| Steel | Low | High |
The table underscores the preferred choices in bonsai wiring.
Best Practices
Employing appropriate wiring techniques is necessary for achieving the desired shape and health of a bonsai tree. When using steel wire, it is important to follow best practices to prevent damage and promote ideal growth.
Here are key guidelines:
- Select the Right Thickness: Choose a wire gauge that is strong enough to hold the branch in place without cutting into the bark.
- Apply Wiring Carefully: Wrap the wire around the branch at a 45-degree angle, ensuring moderate tension to avoid constricting growth.
- Monitor Regularly: Check the wired branches frequently to prevent the wire from embedding into the bark, which can cause scarring.
Adhering to these practices will help you shape your bonsai effectively while maintaining its health and aesthetic appeal.
Conclusion
To sum up, while steel wire boasts impressive strength and durability, its rigidity and potential to damage bonsai trees make it less suitable for wiring compared to aluminum or copper.
Steel wire's lack of flexibility, higher cost, and difficulty of use further limit its practicality for bonsai cultivation. Expert opinions and best practices overwhelmingly favor more pliable and tree-friendly options.
Consequently, for effective and sustainable bonsai wiring, aluminum and copper wires remain the preferred choices.






