Bonsai: Get Lower Branches in 10 Steps
To encourage lower branch development in bonsai, detailed pruning is necessary. Remove apical buds to redistribute auxin, promoting well-rounded growth.
Implement precise wiring using aluminum or copper at a 45-degree angle to shape the branches. Optimize light exposure by rotating the bonsai and using reflective surfaces.
Guarantee a balanced nutrient regimen with nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Consistent soil moisture, high-quality soil mix, and proper pH levels support this growth.
Consider applying growth hormones specifically targeting lower branch enhancement. Understanding the unique requirements of your bonsai species is also essential.
Exploring these techniques in detail maximizes branch development potential.

Key Takeaways
- Prune apical buds to redistribute auxin concentration and encourage lower branch growth.
- Regularly rotate the bonsai for even light exposure to stimulate lower branches.
- Use appropriate wiring techniques to position and support lower branches' development.
- Maintain a balanced nutrient regimen, focusing on nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
- Consistently water the bonsai ensuring soil moisture without root disturbance.
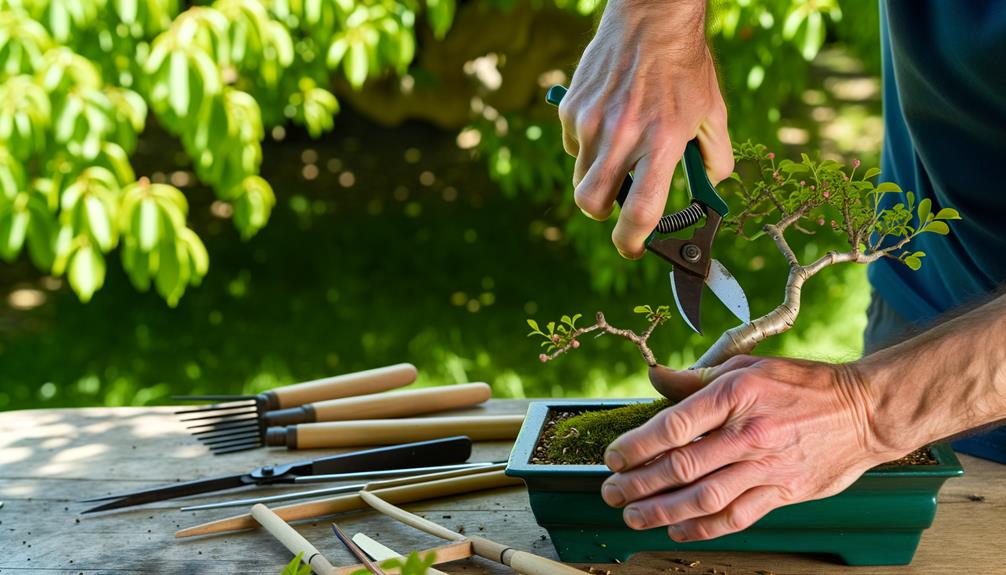
Pruning Techniques

Pruning techniques for encouraging lower branches on a bonsai tree require a detailed approach to selectively removing specific parts of the plant to stimulate growth in the desired areas.
The primary focus should be on the strategic removal of apical buds, which dominate the tree's growth. By trimming these buds, the auxin concentration is redistributed, reducing the hormonal suppression of lower branches and promoting their development.
Additionally, precise cuts should be made above a node where new growth is desired, ensuring a precise cut to prevent disease. Thinning out dense foliage at the canopy can also enhance light penetration to the lower sections.
This methodical pruning guarantees the balanced energy distribution necessary for the best growth of lower branches.
Proper Wiring
Proper wiring techniques are fundamental for guiding the growth direction and structure of lower branches on a bonsai tree, guaranteeing they develop in a balanced and aesthetically pleasing manner. Utilizing precise wiring methods can prevent damage and encourage best growth.
Here are key steps:
- Select Appropriate Wire: Use aluminum or copper wire. Copper is stronger but aluminum is easier to handle.
- Anchor the Wire: Start at the base of the trunk and wrap around, securing it firmly to provide stability.
- Wrap Methodically: Coil the wire at a 45-degree angle, ensuring even spacing and gentle tension to avoid cutting into the bark.
- Monitor Regularly: Check the wire every few weeks, adjusting as necessary to avoid constriction and ensure proper shaping.
These practices are essential for achieving the desired bonsai form.
Light Management

Effective light management is essential for encouraging lower branch development in bonsai. Optimizing light exposure involves ensuring that the lower sections of the tree receive sufficient sunlight, which can be achieved through strategic positioning and periodic rotation of the bonsai.
Additionally, it is important to minimize any obstructions that may block light from reaching the lower branches, thereby promoting uniform growth and vigor.
Optimize Light Exposure
To ensure ideal light exposure for the lower branches of your bonsai, carefully position the tree in a location where it receives balanced and consistent sunlight throughout the day. Ensuring optimal light distribution is essential for promoting even growth and health across all branches.
Consider the following technical guidelines:
- Rotate the Bonsai: Regularly rotate the bonsai to guarantee all sides receive equal sunlight.
- Use Reflective Surfaces: Place reflective materials, such as white boards or foil, around the bonsai to enhance light distribution to lower branches.
- Prune Upper Foliage: Trim the upper canopy strategically to prevent shading of the lower branches.
- Artificial Lighting: Employ grow lights, positioning them to supplement natural light, particularly during shorter winter days.
These measures will foster well-balanced growth and vigor.
Positioning for Branch Growth
Positioning your bonsai to maximize light penetration to the lower branches involves a strategic arrangement that takes into account the tree's natural growth pattern and environmental conditions. To foster lower branch development, rotate the bonsai periodically to guarantee even light distribution across all sides. This prevents the upper foliage from overshadowing the lower branches.
Additionally, consider the angle of sunlight throughout the day; place the tree in a location where morning and afternoon sunlight can reach the lower levels. Enhancing light exposure through the use of reflective surfaces, such as white walls or light-colored stones, can also benefit lower branch growth.
Positioning the bonsai on an elevated stand can further mitigate shading by surrounding objects, ensuring best light conditions.
Avoiding Light Obstructions
Guaranteeing ideal light conditions for lower branch development in bonsai requires meticulous attention to potential obstructions that could inhibit sunlight penetration.
Effective light management is pivotal for fostering robust growth and can be achieved by addressing several key factors:
- Pruning Upper Branches: Regularly prune the upper branches to prevent them from overshadowing the lower sections.
- Rotating the Bonsai: Routinely rotate the bonsai to guarantee even light distribution across all branches.
- Using Reflective Surfaces: Place reflective surfaces around the bonsai to enhance light access to the lower branches.
- Positioning under Grow Lights: Strategically position the bonsai under grow lights to simulate natural sunlight and guarantee consistent illumination.
Nutrient Balance
Maintaining nutrient balance is essential for the best growth and development of bonsai trees, especially when encouraging the formation of lower branches. An ideal nutrient regimen includes nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), each playing a unique role in plant physiology. Nitrogen promotes foliage growth, phosphorus aids in root development, and potassium enhances overall tree vigor.
| Nutrient | Function | Impact on Lower Branches |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Foliage growth | Supports lush leaf production |
| Phosphorus | Root development | Strengthens root system |
| Potassium | Overall vigor and disease resistance | Enhances overall health and resilience |
Achieving the right balance prevents nutrient deficiencies or toxicities that could hinder lower branch development. Regular soil testing and careful fertilizer application are recommended to maintain this balance.
Watering Practices
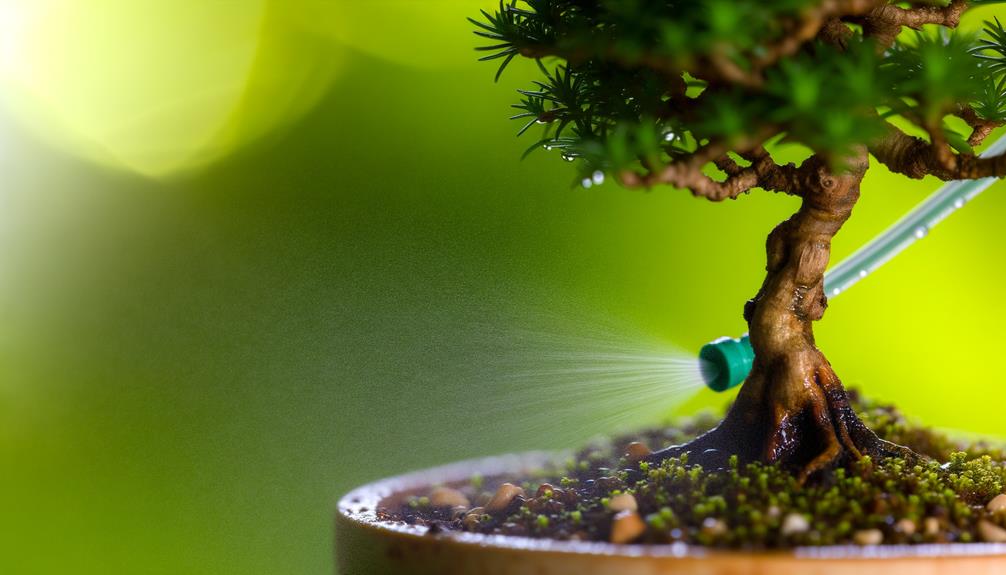

Proper watering practices are essential to the health and development of bonsai trees, particularly when aiming to stimulate the growth of lower branches. Accurate watering methods guarantee sufficient moisture levels, promoting balanced growth throughout the tree.
To achieve best results, consider the following guidelines:
- Consistent Moisture: Maintain uniform soil moisture, avoiding both waterlogging and drought conditions.
- Timing: Water in the early morning or late afternoon to minimize evaporation and maximize absorption.
- Water Quality: Use rainwater or distilled water to prevent mineral buildup, which can impact root health.
- Technique: Utilize a fine spray nozzle to deliver water gently, preventing soil displacement and root disturbance.
These practices create a favorable environment for the development of lower branches, ensuring a well-balanced and healthy bonsai tree.
Soil Quality
Improving soil quality is crucial for the successful cultivation and growth of lower branches on bonsai trees. High-grade soil guarantees sufficient root aeration, proper water retention, and necessary nutrient availability.
A well-balanced bonsai soil mix typically consists of akadama, pumice, and lava rock. Akadama, a type of clay, retains moisture and nutrients, while pumice enhances aeration and drainage. Lava rock contributes to overall soil structure stability.
The pH level should be slightly acidic to neutral, around 6.0 to 7.0, to promote best nutrient uptake. Regularly sifting the soil to remove fines prevents compaction, maintaining root health. Utilizing such a customized soil composition is crucial to promoting strong lower branch development.
Growth Hormones
In addition to optimizing soil quality, the application of growth hormones can greatly enhance the development of lower branches on bonsai trees by regulating cellular activities and promoting targeted growth. Key growth hormones, such as auxins and cytokinins, play critical roles in this process.
Auxins, primarily concentrated at the apical meristem, can be redirected to lower branches to stimulate growth. Cytokinins, which promote cell division, can be applied to lower areas to encourage branching.
To effectively use growth hormones:
- Identify appropriate hormone types: Choose between auxins, cytokinins, or gibberellins.
- Determine correct concentrations: Apply precise dosages to avoid plant stress.
- Timing of application: Apply during active growth periods.
- Monitor and adjust: Continually assess plant response and make necessary adjustments.
Species Selection
Selecting the appropriate bonsai species is crucial for successful lower branch development. Different species exhibit varying growth patterns and responses to cultivation techniques. Deciduous species, such as Japanese Maple (Acer palmatum), often display vigorous lower branching under proper pruning and environmental conditions.
Conversely, coniferous species like Juniper (Juniperus spp.) may require more intensive wiring and shaping to encourage lower branch formation. Tropical species, including Ficus (Ficus retusa), generally offer more flexibility due to their year-round growth cycle and robust response to defoliation.
Understanding each species' specific requirements for light, humidity, and soil composition is essential. Selecting species known for resilient lower branch growth can greatly enhance your ability to cultivate a well-balanced and aesthetically pleasing bonsai.
Patience and Observation

Cultivating lower branches in bonsai demands a diligent practice of patience and meticulous observation. Understanding the tree's growth patterns and responses to various techniques is essential for successful development. By closely monitoring the tree's behavior, practitioners can make informed decisions to promote the growth of lower branches effectively.
Key actions include:
- Regular Monitoring: Observe the tree frequently to identify signs of new growth or potential issues.
- Pruning Techniques: Apply selective pruning to redirect energy towards lower branches.
- Light Management: Guarantee lower branches receive adequate sunlight by adjusting the tree's position.
- Nutrient Distribution: Balance fertilization to support overall health while encouraging lower branch development.
Such disciplined practices allow for the precise cultivation of aesthetically pleasing bonsai with well-developed lower branches.
Conclusion
Achieving lower branches in bonsai requires an integrated approach:
precise pruning techniques, meticulous wiring, best light management, balanced nutrients, consistent watering practices, high-quality soil, and appropriate growth hormones.
Species selection must align with desired growth characteristics, while patience and keen observation remain pivotal.
Each factor contributes synergistically, ensuring a harmonious development of lower branches. Mastery of these elements will lead to a well-balanced, aesthetically pleasing bonsai, reflecting both art and science in cultivation.



